SSO Providers
The platform supports all major Single-Sign-On (SSO) providers. To configure SSO for the platform, expand the desired SSO provider (for example Google, Okta, GitHub) field listed below and follow the instructions provided.
Most SSO provider connections do not allow localhost and require that you
set up a domain for your platform instance first.
Providers
GitHub
Create A GitHub App
GitHub Apps allow external services to authenticate users through GitHub's OAuth system. To set up SSO for the platform, create a new OAuth App in GitHub:
-
Navigate to
Settings > Developer Settings > OAuth Appsin GitHub. -
Click on Create a new OAuth App.
-
Configure the OAuth App with the following settings:
- Application name: Platform Login via GitHub
- Homepage URL:
https://$VCLUSTER_PRO_HOSTNAME - Authorization callback URL:
https://$VCLUSTER_PRO_HOSTNAME/auth/github/callback
-
After creating the app, note the
$GITHUB_CLIENT_IDand$GITHUB_CLIENT_SECRET. These is required in the next step.
infoReplace
$VCLUSTER_PRO_HOSTNAMEwith your actual platform hostname.-
Create platform config for GitHub
To enable GitHub SSO for the platform, use the following YAML configuration to update your platform config (the
configsection of thevalues.yaml) or through vCluster Platform UI Admin > Config:GitHub SSO Configurationauth:
# Tell loft to use github authentication
github:
#
#
# REQUIRED CONFIGURATION
#
#
# ClientID of the github application. Can be string literal or pulled from the environment.
clientId: $GITHUB_CLIENT_ID
# ClientSecret of the github application. Can be string literal or pulled from the environment.
clientSecret: $GITHUB_CLIENT_SECRET
# Callback URL in the form of https://your-loft-domain/auth/github/callback
redirectURI: https://vcluster-platform.my.domain/auth/github/callback
#
#
# OPTIONAL CONFIGURATION
#
#
# (Optional) vCluster Platform queries the following organizations for group information.
# Group claims are formatted as "(org):(team)".
# For example if a user is part of the "engineering" team of the "coreos"
# org, the group claim would include "coreos:engineering".
#
# If orgs are specified in the config then user MUST be a member of at least one
# of the specified orgs to authenticate with loft.
orgs:
# Organization name in github (not slug, full name)
- name: My Organization
# (Optional) Names of teams in a github organization. A user will be able to
# authenticate if they are members of at least one of these teams.
teams:
- myteam
# (Optional) Required ONLY for GitHub Enterprise.
# This is the Hostname of the GitHub Enterprise account listed on the
# management console.
hostName: my-github.org
# (Optional) Required ONLY for GitHub Enterprise.
# Used to support self-signed or untrusted CA root certificates.
rootCA: /certs/github.caConfiguration options explained:
clientId: The Client ID from the GitHub OAuth App.clientSecret: The Client Secret from the GitHub OAuth App.redirectURI: The Authorization callback URL specified in the GitHub OAuth App.orgs: Specify GitHub organizations and teams allowed to access the platform.hostName: Custom GitHub Enterprise hostname (if applicable).rootCA: Path to a custom root certificate for GitHub Enterprise (if applicable).
Authenticate via GitHub
After saving the new configuration, the platform should restart. Users can now log in via GitHub:
- Access the platform login page.
- Click on the "Login with GitHub" option.
- Authenticate with GitHub credentials.
- Grant the requested permissions to the GitHub OAuth App.
warningUsers must grant access to the organization configured in step 2. Without this access, they are not going to be able to log in.
Disable Username + Password Authentication (optional)
To turn off password-based authentication, navigate to
Admin > Configadd these two lines to your config:Disable password-based authenticationauth:
oidc: ... # This is your SSO configuration (make sure this is working!)
password:
disabled: true # Disable password-based authentication
OIDC
OIDC authentication
OpenID Connect Specification is an authentication layer built on top of OAuth 2.0, providing secure and standardized user authentication for applications. Implementing OIDC in the platform offers several benefits:
- Enhanced security through token-based authentication
- Simplified user management with centralized identity providers
- Improved user experience with
single sign-on(SSO) capabilities
Create platform config for OIDC
To configure OIDC for SSO, use the following YAML configuration to update your platform config (the
configsection of thevalues.yaml) or through vCluster Platform UI Admin > Config:Platform OIDC configurationauth:
# Tell vCluster Platform to allow OIDC for authentication
oidc:
#
#
# REQUIRED CONFIGURATION
#
#
# IssuerURL is the URL the provider signs ID Tokens as.
# If using Keycloak provide the realm as well, only providing the base URL will return a 404. Ex. https://your-keycloak/realms/YOUR-REALM
issuerUrl: https://accounts.google.com
# ClientID the JWT must be issued for, the "sub" field. Can be string literal or pulled from the environment.
clientId: $CLIENTID
# ClientSecret to issue tokens from the OIDC provider. Can be string literal or pulled from the environment.
clientSecret: $CLIENTSECRET
# Callback URL in the form of https://your-loft-domain/auth/oidc/callback
redirectURI: https://vcluster-platform.my.domain/auth/oidc/callback
#
#
# OPTIONAL CONFIGURATION
#
#
# (Optional) Path to a PEM encoded root certificate of the provider.
caFile: /tmp/ca-file.crt
# (Optional) Specify whether to communicate without validating SSL certificates
insecureCa: false
# (Optional) UsernameClaim is the JWT field to use as the user's username.
# If not set defaults to email.
usernameClaim: email
# (Optional) If specified, causes claims mapping to username to be prefix with
# the provided value.
usernamePrefix: my-prefix-
# (Optional) If specified, causes the OIDCAuthenticator to try to populate the user's
# groups with an ID Token field.
groupsClaim: groups
# (Optional) If specified, causes claims mapping to group names to be prefixed with the
# value.
groupsPrefix: group-prefix-
# (Optional) If groups is non empty, access is denied if the user is not part of at least one
# of the specified groups. This requires groupsClaim to be set!
groups: ["my-oidc-group"]
# (Optional) If specified, tells the OIDCAuthenticator to try to populate the user's
# information from the UserInfo. This might be necessary for slim tokens such as used
# by Okta
getUserInfo: false
# (Optional) Scopes that should be sent to the server. If empty, defaults to "email" and "profile".
scopes: ["profile", "email"]
# (Optional) EmailClaim is the JWT field to use as the user's email.
emailClaim: "email"
# (Optional) vCluster PlatformUsernameClaim is the JWT field to use as the user's ID (Kubernetes name) and username
loftUsernameClaim: "name"
# (Optional) PreferredUsername is the JWT field to use as the user's display name
preferredUsername: "preferred_username"
# (Optional) AllowedExtraClaims are claims of interest that are provided by the OIDC provider but may not already be
# covered by a User field. These additional claims of interest will be copied to User.Spec.ExtraClaims.
# Like other claims, User.Spec.ExtraClaims is only updated when the User logs in using the OIDC provider. A user must
# login after changes to AllowedExtraClaims for them to be reflected in a User's User.Spec.ExtraClaims.
allowedExtraClaims: ["department"]Obtaining OIDC credentialsTo obtain the required
clientIdandclientSecret, refer to your OIDC provider's documentation. Common providers include:Authenticate via OIDC
After saving the new configuration, the platform should restart. You should then be able to log in via your OIDC provider.
Disable Username + Password Authentication (optional)
To turn off password-based authentication, navigate to
Admin > Configadd these two lines to your config:Disable password-based authenticationauth:
oidc: ... # This is your SSO configuration (make sure this is working!)
password:
disabled: true # Disable password-based authentication
GitLab
This guide explains how to integrate GitLab Single Sign-On (SSO) with the platform, allowing users to authenticate using their GitLab credentials.
Create A GitLab App
Navigate to the GitLab User Settings > Applications page and create a new application with the following settings:
- Application name: Platform Login via GitLab
- Redirect URI: https://vcluster-platform.yourcompany.tld/auth/gitlab/callback =
https:// + $VCLUSTER_PRO_HOSTNAME + /auth/gitlab/callback - Scopes:
read_user+openid
infoGitLab generates a
$GITLAB_CLIENT_IDand$GITLAB_CLIENT_SECRETfor your OAuth application. These credentials are required for the next step.Create Platform config For GitLab
To set up GitLab SSO in the platform, use the following YAML configuration to update your platform config (the
configsection of thevalues.yaml) or through vCluster Platform UI Admin > Config:GitLab SSO configurationauth:
# Tell loft to use gitlab authentication
gitlab:
#
#
# REQUIRED CONFIGURATION
#
#
# ClientID for the gitlab authentication. Can be string literal or pulled from the environment.
clientId: $GITLAB_CLIENT_ID
# ClientSecret for the gitlab authentication. Can be string literal or pulled from the environment.
clientSecret: $GITLAB_CLIENT_SECRET
# Callback URL in the form of https://your-loft-domain/auth/gitlab/callback
redirectURI: https://vcluster-platform.my.domain/auth/gitlab/callback
#
#
# OPTIONAL CONFIGURATION
#
#
# (Optional) BaseURL of the gitlab instance,
# default = https://gitlab.com
baseURL: https://my-gitlab-instance.com
# (Optional) Optional groups whitelist, communicated through the "groups" scope.
# If groups is omitted, all of the user's GitLab groups are returned.
# If groups is provided, this acts as a whitelist - only the user's GitLab
# groups that are in the configured groups below will go into the groups claim.
# Conversely, if the user is not in any of the configured groups, the user will
# not be authenticated.
groups:
- my-groupAuthenticate via GitLab
After saving the new configuration, the platform should restart automatically. Users can now log in using their GitLab credentials.
Disable Username + Password Authentication (optional)
To turn off password-based authentication, navigate to
Admin > Configadd these two lines to your config:Disable password-based authenticationauth:
oidc: ... # This is your SSO configuration (make sure this is working!)
password:
disabled: true # Disable password-based authentication
Microsoft
Create platform config for Microsoft
The platform is able to use Microsoft Single Sign-On (SSO) OAuth2 flow to identify the end user through their Microsoft account.
Tenant Must Be Specified in Microsoft Connector Config to Sync SSO GroupsThe groups claim is only supported when tenant is specified in Microsoft connector config. Furthermore, tenant must also be configured to either
<tenant uuid> or <tenant name>. In order for the platform to be able to list groups on behalf of logged in user, an explicit organization administrator consent is required. To obtain the consent do the following:The platform can use Microsoft OAuth2 flow to identify end users through their Microsoft accounts.
The groups claim is only supported when the tenant is specified in the Microsoft connector config. The tenant must be configured to either
<tenant uuid>or<tenant name>. For the platform to list groups on behalf of the logged-in user, explicit organization administrator consent is required. To obtain consent:- When registering the platform application on https://apps.dev.microsoft.com, add an explicit Directory.Read.All permission to the list of Delegated Permissions.
- Open the following link in your browser and log in under an organization administrator account:
https://login.microsoftonline.com/<tenant>/adminconsent?client_id=<client id>To configure the platform to use Microsoft for SSO, use the following YAML configuration to update your platform config (the
configsection of thevalues.yaml) or through vCluster Platform UI Admin > Config:Microsoft SSO configurationauth:
# Tell the platform to use microsoft authentication
microsoft:
#
#
# REQUIRED CONFIGURATION
#
#
# ClientID of the microsoft application. Can be string literal or pulled from the environment.
clientId: $CLIENTID
# ClientSecret of the microsoft application. Can be string literal or pulled from the environment.
clientSecret: $CLIENTSECRET
# Callback URL in the form of https://your-loft-domain/auth/microsoft/callback
redirectURI: https://vcluster-platform.my.domain/auth/microsoft/callback
#
#
# OPTIONAL CONFIGURATION
#
#
# (Optional) tenant configuration parameter controls what kinds of accounts
# may be authenticated in loft. By default, all types of Microsoft
# accounts (consumers and organizations) can authenticate in loft via Microsoft.
# To change this, set the tenant parameter to one of the following:
# common - both personal and business accounts can authenticate via Microsoft (default)
# consumers - only personal accounts can authenticate in loft
# organizations - only business/school accounts can authenticate in loft
# 'tenant uuid' or 'tenant name' - only accounts belonging to specific tenant
# identified by either 'tenant uuid' or 'tenant name' can authenticate in loft
tenant: common
# (Optional) It is possible to require a user to be a member of a particular
# group in order to be successfully authenticated in loft.
groups: []
# (Optional) Configuration option restricts the list to include only security groups.
# By default all groups (security, Office 365, mailing lists) are included.
onlySecurityGroups: false
# (Optional) Restrict the groups claims to include only the user’s groups
# that are in the configured groups
useGroupsAsWhitelist: falseOptional configuration parameterstenant: Controls what kinds of accounts may be authenticated. Options include:common: Both personal and business accounts (default)consumers: Only personal accountsorganizations: Only business/school accounts'tenant uuid'or'tenant name': Only accounts belonging to a specific tenant
groups: Require users to be members of specific groups for authenticationonlySecurityGroups: Restricts the list to include only security groupsuseGroupsAsWhitelist: Restricts the groups claims to include only the user's groups that are in the configured groups
Obtaining ClientID and ClientSecretTo obtain the
$CLIENTIDand$CLIENTSECRETvalues:- Register your application in the Azure Portal
- Navigate to "App registrations"
- Select your application and find the "Application (client) ID" for
$CLIENTID - Under "Certificates & secrets", create a new client secret for
$CLIENTSECRET
Authenticate via Microsoft
After saving the new platform configuration, the platform should restart. Users should then be able to log in via Microsoft.
Disable Username + Password Authentication (optional)
To turn off password-based authentication, navigate to
Admin > Configadd these two lines to your config:Disable password-based authenticationauth:
oidc: ... # This is your SSO configuration (make sure this is working!)
password:
disabled: true # Disable password-based authentication
Introduction
Google Single Sign-On (SSO) allows users to access the platform using their Google credentials. This integration enhances security and simplifies user management by leveraging Google's authentication infrastructure.
Prerequisites
Before setting up Google SSO, ensure you have:
- A Google Account with admin privileges
- Administrator access to the platform
- Access to GPC console for creating OAuth2.0 credentials
Configuration steps
Create platform config for Google
The platform can use Google's OpenID Connect provider as an authentication source.
Obtaining Google OAuth2.0 credentialsTo get the required
clientIdandclientSecret, follow these steps:- Go to the GCP Console
- Navigate to "APIs & Services" > "Credentials"
- Click "Create Credentials" and select "OAuth client ID"
- Follow the prompts to set up your OAuth consent screen and create your credentials
To configure the platform to use Google for SSO, use the following YAML configuration to update your platform config (the
configsection of thevalues.yaml) or through vCluster Platform UI Admin > Config:Google SSO Configurationauth:
# Tell vCluster Platform to use google authentication
google:
#
#
# REQUIRED CONFIGURATION
#
#
# ClientID for the google authentication. Can be string literal or pulled from the environment.
clientId: $CLIENTID
# ClientSecret for the google authentication. Can be string literal or pulled from the environment.
clientSecret: $CLIENTSECRET
# Callback URL in the form of https://your-loft-domain/auth/google/callback
redirectURI: https://vcluster-platform.my.domain/auth/google/callback
#
#
# OPTIONAL CONFIGURATION
#
#
# (Optional) defaults to "profile" and "email"
scopes: ["profile", "email"]
# (Optional) list of whitelisted domains. If this field is nonempty,
# only users from a listed domain will be allowed to log in
hostedDomains: []
# (Optional) list of whitelisted groups. If this field is nonempty,
# only users from a listed group will be allowed to log in
groups: []
# (Optional) path to service account json. If nonempty,
# and groups claim is made, will use authentication from file to
# check groups with the admin directory api
serviceAccountFilePath: /path/to/service/account.json
# (Optional) Required if serviceAccountFilePath is set. The email of
# a GSuite super user which the service account will impersonate
# when listing groups
adminEmail: myuser@mydomain.comSecurity best practiceAlways store sensitive information like
clientSecretsecurely. Consider using environment variables or secure secret management solutions.noteReplace the
redirectURIwith your actual domain where the platform is hosted.Authenticate via Google
After saving the new configuration, the platform should restart itself. To authenticate:
- Navigate to the platform login page
- Click on the "Login with Google" button
- You should be redirected to Google's login page
- Enter your Google credentials
- Grant the necessary permissions when prompted
- You should be redirected back to the platform, now authenticated
Disable Username + Password Authentication (optional)
To turn off password-based authentication, navigate to
Admin > Configadd these two lines to your config:Disable password-based authenticationauth:
oidc: ... # This is your SSO configuration (make sure this is working!)
password:
disabled: true # Disable password-based authentication
Okta
This guide walks you through the process of setting up Single Sign-On (SSO) with Okta for the platform. By following these steps, you'll enable seamless authentication for your users through Okta.
Create A New App In Okta
Start by creating a new Okta App for the platform.

Okta - Create a new App in Okta Select "Web" App and ensure OpenID Connect is the single sign-on method.
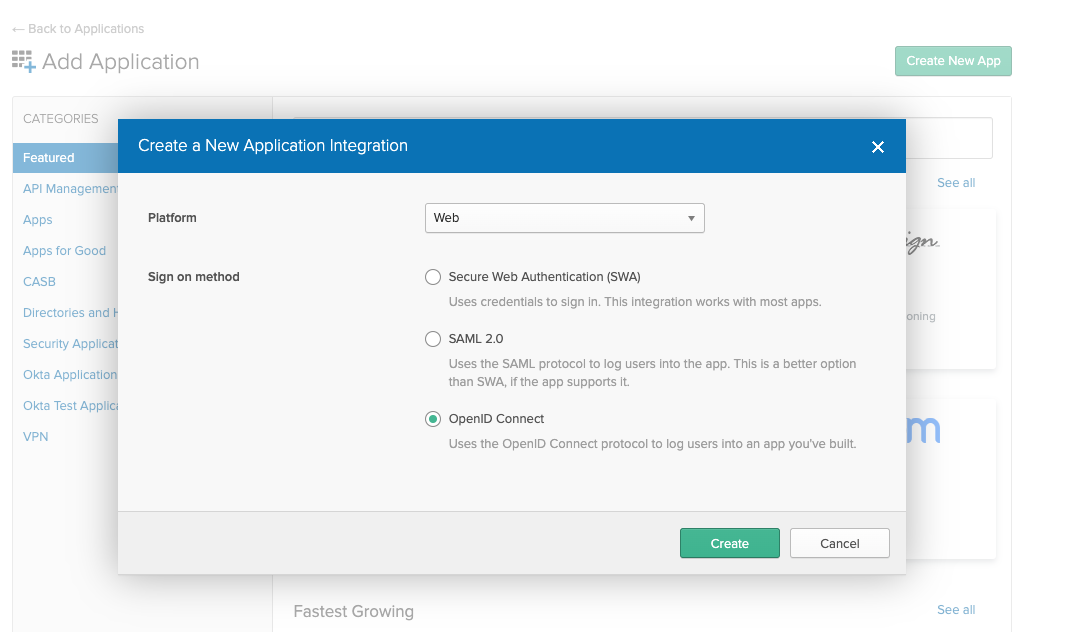
Okta - Web App with OpenID Connect as single sign on method
On the next screen, configure the login redirect URIs to include your platform instance domain:
Configure login redirect URI# Replace ${my-loft-domain.com} with your platform domain
https://${my-loft-domain.com}/auth/oidc/callback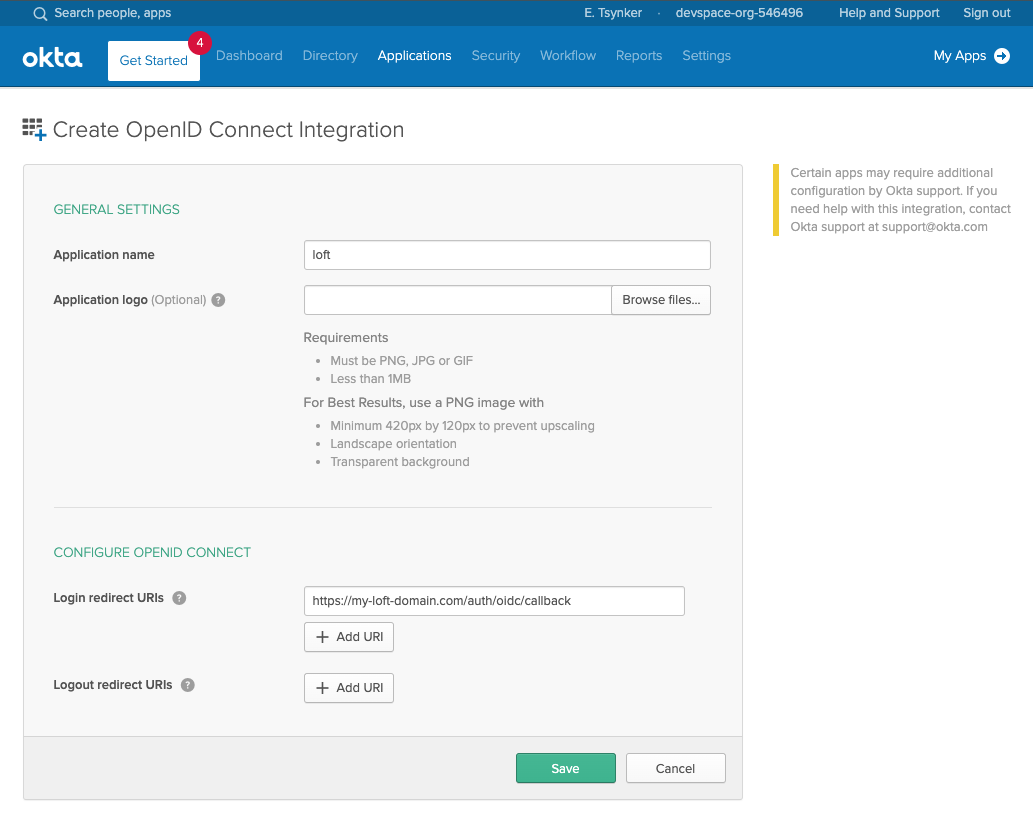
Okta - The App settings for the platform Enable Refresh Tokens
After creating the Okta app for the platform, enable "Refresh Token" under "Allowed grant types". This step is crucial as it allows users to maintain their session without frequent re-logins.
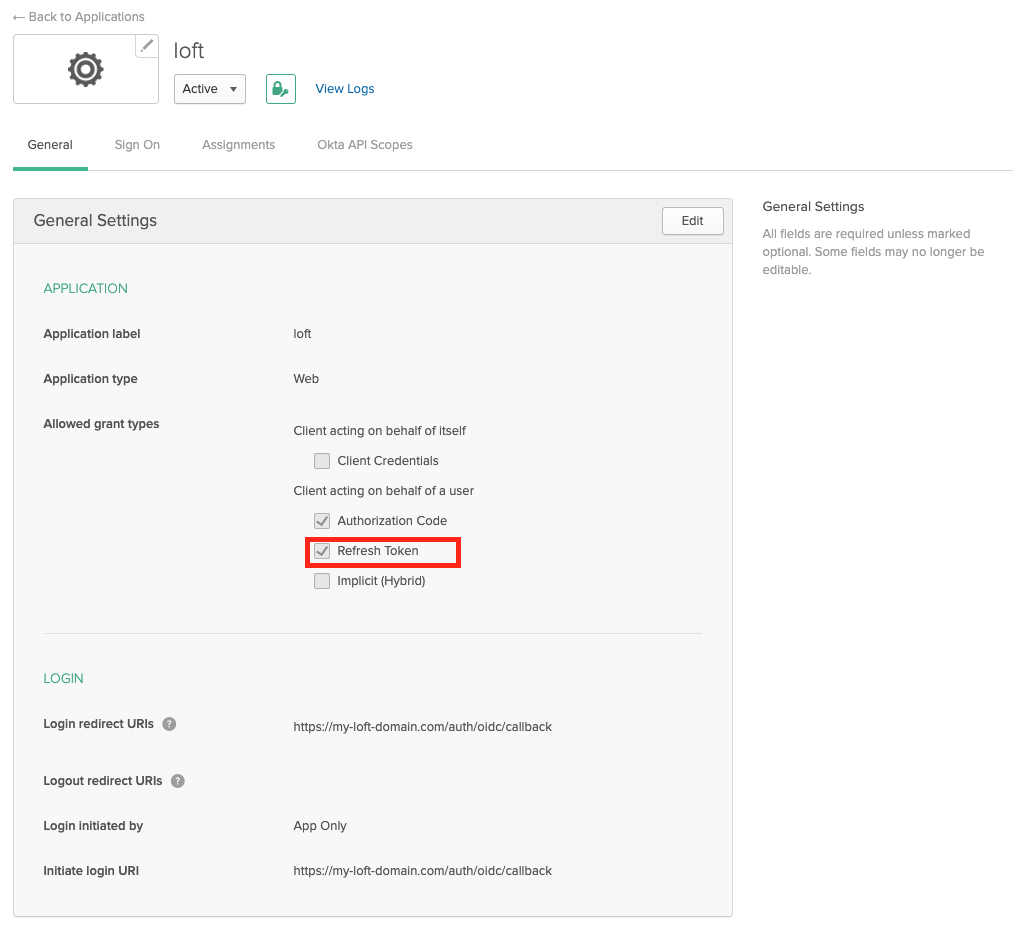
Okta - App Settings: Enable Refresh Tokens Enable Group Claims
If you want to propagate the users groups to the platform, then make sure the Group Filters in Okta are set accordingly. If you want to propagate all groups, add a RegEx filter with '.*'
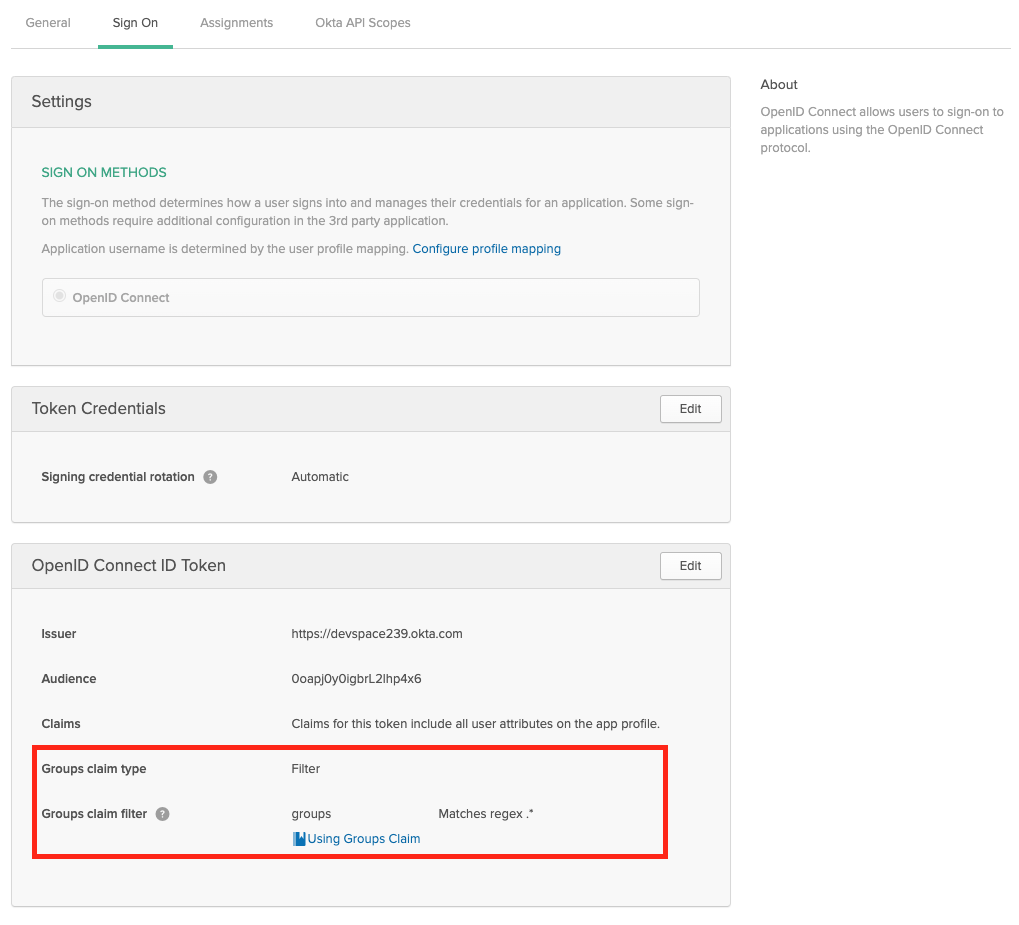
Okta - Propagate User Groups To the platform Configure platform to use Okta
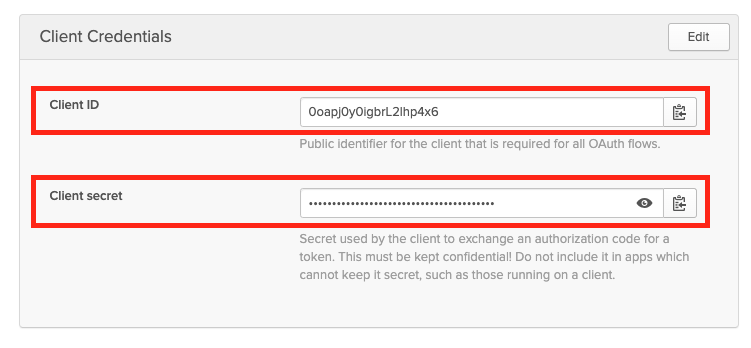
Okta - Client ID and Secret For App Navigate to
Admin > Configin the platform and enter the following configuration:Configure the platform for Okta integrationauth:
oidc:
issuerUrl: "https://${MY-OKTA-SUBDOMAIN}.okta.com"
clientId: CLIENT_ID
clientSecret: CLIENT_SECRET
groupsClaim: groups
# This is needed because Okta uses thin id tokens
# that do not contain the groups directly
getUserInfo: trueThe
groupsClaimfield specifies where to find group information in the token, andgetUserInfois set totrueto retrieve additional user information from Okta.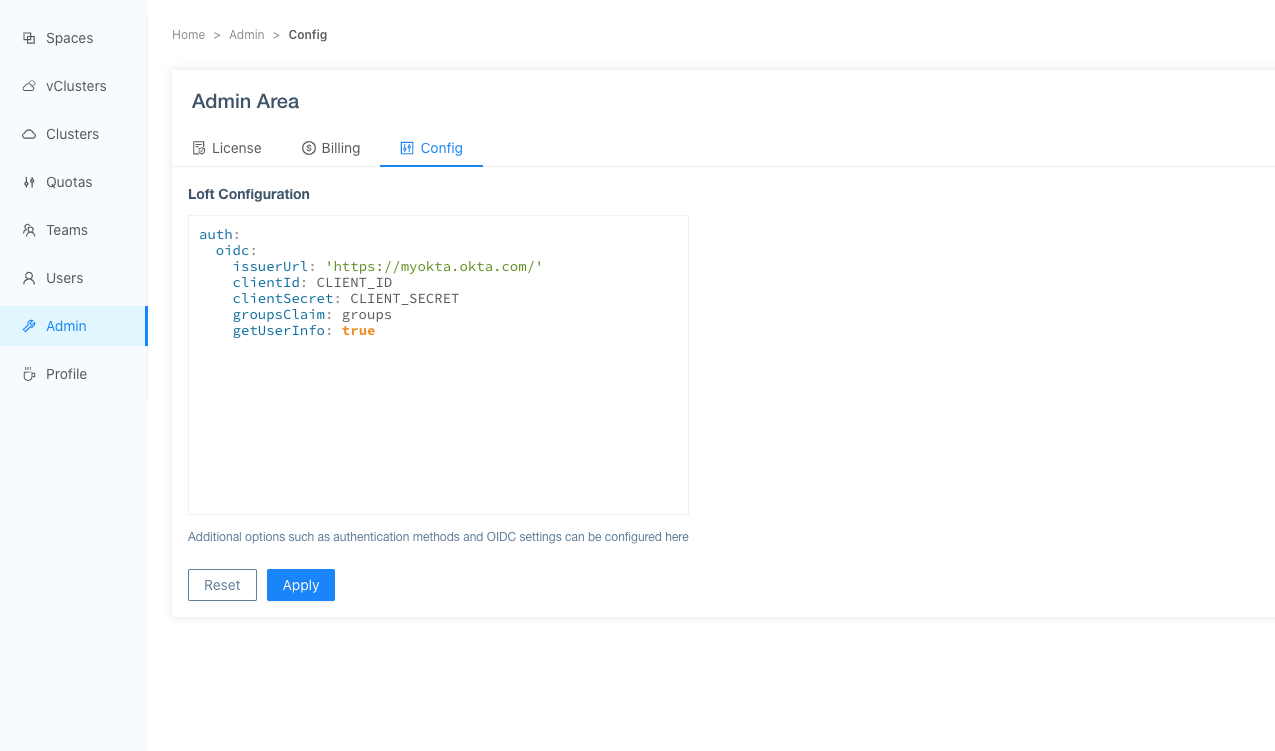
Configure the platform To Use Okta Add Users via Okta Assigments
Assign the appropriate Users and Groups to access the platform in Okta.
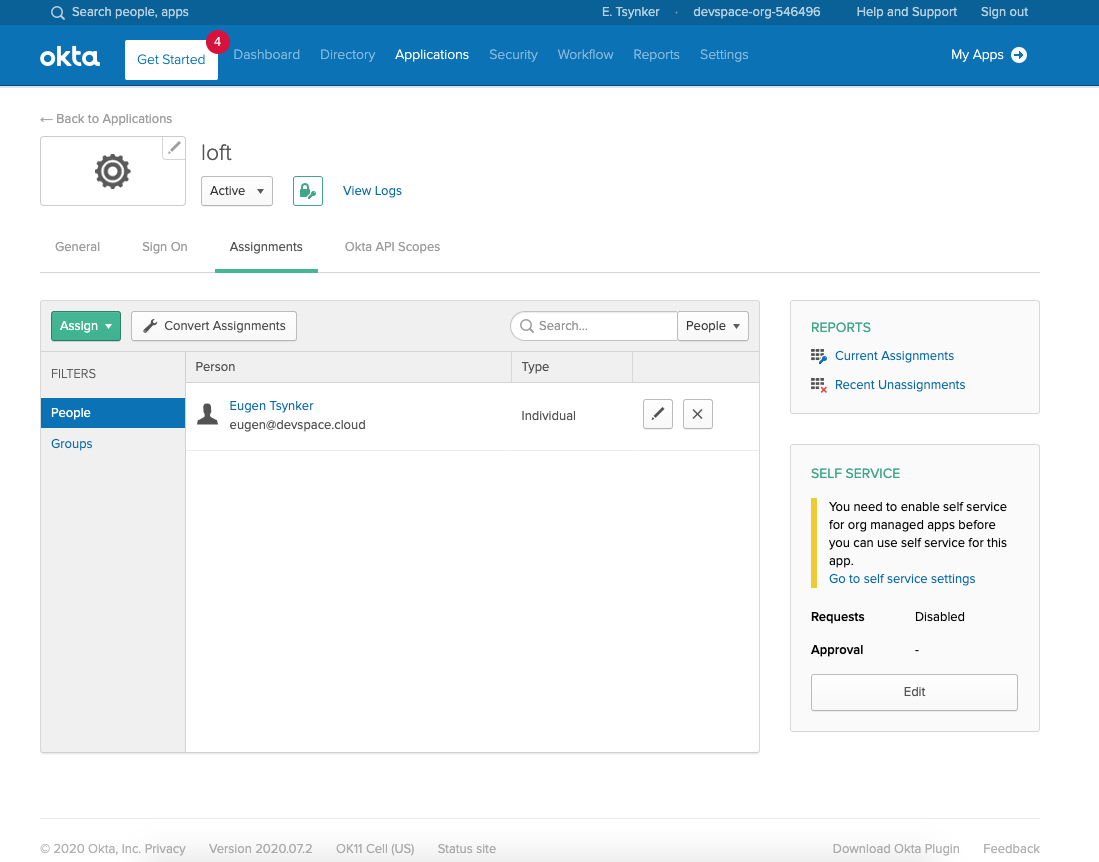
Okta - Assign Users & Groups To the platform Once users or their groups are assigned to the platform, they can log in via Okta:
The platform - SSO via Okta Disable Username + Password Authentication (optional)
To turn off password-based authentication, navigate to
Admin > Configadd these two lines to your config:Disable password-based authenticationauth:
oidc: ... # This is your SSO configuration (make sure this is working!)
password:
disabled: true # Disable password-based authentication
SAML 2.0
Introduction to SAML authentication
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) Specification is an open standard for exchanging authentication and authorization data between parties, particularly between an identity provider and a service provider. SAML is useful for implementing secure single sign-on (SSO) in enterprise environments, allowing users to access multiple applications with a single set of credentials.
The SAML 2.0 connector in the platform does not support refresh tokens as the SAML 2.0 protocol does not provide a way to requery a provider without interaction. For more information, see the dex documentation for SAML 2.0.
Create platform Config For SAML v2.0
The platform can use SAML v2.0 flow to identify the end user. To configure the platform to use SAML for SSO, follow these steps:
- Use the following YAML configuration to update your platform config (the
configsection of thevalues.yaml) or through vCluster Platform UI Admin > Config: - Obtain the necessary values from your SAML identity provider (IdP) for the required fields.
Configure the platform to use SAMLauth:
# Tell vCluster Platform to use saml authentication
saml:
#
#
# REQUIRED CONFIGURATION
#
#
# SSO URL used for POST value.
ssoURL: https://saml.example.com/sso
# CA to use when validating the signature of the SAML response.
ca: /path/to/ca.pem
# Alternatively, CA can be provided inline as a base64-encoded blob
# caData: (RAW base64-encoded PEM encoded CA)
# Callback URL in the form of https://your-vcluster-platform-domain/auth/saml/callback
redirectURI: https://vcluster-platform.my.domain/auth/saml/callback
# Name of attributes in the returned assertions to map to ID token claims.
usernameAttr: name
emailAttr: email
groupsAttr: groups # optional
#
#
# OPTIONAL CONFIGURATION
#
#
# (Optional) List of groups to filter access based on membership
allowedGroups: ["Admins"]
# (Optional) To skip signature validation, uncomment the following field. This should
# only be used during testing and may be removed in the future
insecureSkipSignatureValidation: true
# (Optional) Manually specify vCluster Platform's Issuer value.
# When provided vCluster Platform will include this as the Issuer value during AuthnRequest.
# It will also override the redirectURI as the required audience when evaluating
# AudienceRestriction elements in the response.
entityIssuer: https://vcluster-platform.my.domain/auth/saml/callback
# (Optional) Issuer value expected in the SAML response.
ssoIssuer: https://saml.example.com/sso
# (Optional) Delimiter for splitting groups returned as a single string.
#
# By default, multiple groups are assumed to be represented as multiple
# attributes with the same name.
#
# If "groupsDelim" is provided groups are assumed to be represented as a
# single attribute and the delimiter is used to split the attribute's value
# into multiple groups.
groupsDelim: ", "
# (Optional) Requested format of the NameID.
#
# The NameID value is is mapped to the user ID of the user. This can be an
# abbreviated form of the full URI with just the last component. For example,
# if this value is set to "emailAddress" the format will resolve to:
#
# urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:1.1:nameid-format:emailAddress
#
# If no value is specified, this value defaults to:
#
# urn:oasis:names:tc:SAML:2.0:nameid-format:persistent
#
nameIDPolicyFormat: persistent- Use the following YAML configuration to update your platform config (the
Authenticate via SAML
- The platform should restart automatically.
- You should now be able to log in via SAML.
- Test the authentication by logging out and logging back in.
Disable Username + Password Authentication (optional)
To turn off password-based authentication, navigate to
Admin > Configadd these two lines to your config:Disable password-based authenticationauth:
oidc: ... # This is your SSO configuration (make sure this is working!)
password:
disabled: true # Disable password-based authentication
LDAP
Choose DEX_HOSTNAME And Configure DNS
The platform uses the CNCF project dex for single sign-on.
The easiest case is this one:
$VCLUSTER_PRO_HOSTNAME = vcluster-platform.mycompany.tld(where platform is running)$DEX_HOSTNAME = dex.mycompany.tld(where dex should be running)
Create Dex Config For LDAP
Create the file
dex-config.yamlwith the following dex configuration:ingress:
enabled: true
hosts:
- host: dex.yourcompany.tld # Use $DEX_HOSTNAME
paths:
- path: /
config:
issuer: https://dex.yourcompany.tld # "https://" + $DEX_HOSTNAME
connectors:
- type: ldap
id: ldap
name: LDAP
config:
host: myldap.company.tld:636 # Your LDAP server hostname:port
# insecureNoSSL: true # Not recommended but required if not using TLS (port 389)
# insecureSkipVerify: true # Not recommended but required for self-signed certificates
# rootCAData: ( base64 encoded PEM file )
# startTLS: true # Use ldap:// instead of ldaps:// protocol
# The DN and password for an application service account. The connector uses
# these credentials to search for users and groups. Not required if the LDAP
# server provides access for anonymous auth.
# Please note that if the bind password contains a `$`, it has to be saved in an
# environment variable which should be given as the value to `bindPW`.
bindDN: uid=serviceaccount,cn=users,dc=example,dc=com
bindPW: password
# User search maps a username and password entered by a user to a LDAP entry.
userSearch:
# BaseDN to start the search from. It will translate to the query
# "(&(objectClass=person)(uid=<username>))".
baseDN: cn=users,dc=example,dc=com
# Optional filter to apply when searching the directory.
filter: "(objectClass=person)"
# username attribute used for comparing user entries. This will be translated
# and combined with the other filter as "(<attr>=<username>)".
username: uid
# The following three fields are direct mappings of attributes on the user entry.
# String representation of the user.
idAttr: uid
# Required. Attribute to map to Email.
emailAttr: mail
# Maps to display name of users. No default value.
nameAttr: name
# Group search queries for groups given a user entry.
groupSearch:
# BaseDN to start the search from. It will translate to the query
# "(&(objectClass=group)(member=<user uid>))".
baseDN: cn=groups,dc=freeipa,dc=example,dc=com
# Optional filter to apply when searching the directory.
filter: "(objectClass=group)"
# Represents group name.
nameAttr: name
# Following list contains field pairs that are used to match a user to a group. It adds an additional
# requirement to the filter that an attribute in the group must match the user's
# attribute value.
userMatchers:
- userAttr: uid
groupAttr: member
staticClients:
- name: vCluster Platform
id: loft # Define a $DEX_CLIENT_ID
secret: XXXXXXXXXXXXXX # Define a $DEX_CLIENT_SECRET (can be any secret key)
redirectURIs:
- "https://vcluster-platform.mycompany.tld/auth/oidc/callback" # vCluster Platform URL + /auth/oidc/callback
oauth2:
skipApprovalScreen: true
web:
http: 0.0.0.0:5556
storage:
type: kubernetes
config:
inCluster: trueFor details about configuring dex for LDAP, take a look at the dex documentation for LDAP.
Deploy Dex via Helm
After creating the file
dex-config.yaml, you can now install dex via Helm:helm install dex dex --repo https://charts.dexidp.io \
--create-namespace --namespace dex \
-f dex-config.yaml \
--waitConfigure the platform to use dex for authentication
To tell the platform to use dex for SSO, navigate to
Admin > Configin the platform and adjust your config as shown below:Platform OIDC config for dexauth:
oidc:
issuerUrl: https://dex.mycompany.tld # Use $DEX_HOSTNAME (see above)
clientId: "" # Use $DEX_CLIENT_ID (see above)
clientSecret: "" # Use $DEX_CLIENT_SECRET (see above)
type: "github" # Optional: SSO Login Button Icon ("", github, gitlab, microsoft, google)
usernameClaim: "email" # Optional: Which part of the dex token to use as vCluster Platform username (default: email)
usernamePrefix: "" # Optional: Add prefix to usernameClaim for vCluster Platform username
groupsClaim: "groups" # Optional: Add Kubernetes groups for this user
groupsPrefix: "loft-" # Optional: Prefix for Kubernetes groups
caFile: "" # Optional: Path to a CA cert of dex within the vCluster Platform container (default: '')Authenticate via Dex + LDAP
After saving the new platform configuration, the platform is going to restart itself and you should be able to log in via LDAP and dex.
Disable Username + Password Authentication (optional)
To turn off password-based authentication, navigate to
Admin > Configadd these two lines to your config:Disable password-based authenticationauth:
oidc: ... # This is your SSO configuration (make sure this is working!)
password:
disabled: true # Disable password-based authentication
Other (OpenShift, LinkedIn ...)
Platform supports a variety of other auth providers. You can follow this generic guide to configure SSO for any of the auth providers, including:
- OpenShift
- AuthProxy
- Bitbucket Cloud
- Atlassian Crowd
- Gitea
Choose DEX_HOSTNAME And Configure DNS
The platform uses the CNCF project dex for single sign-on.
The easiest case is this one:
$VCLUSTER_PRO_HOSTNAME = vcluster-platform.mycompany.tld(where platform is running)$DEX_HOSTNAME = dex.mycompany.tld(where dex should be running)
Create Dex Config For $OTHER_PROVIDER
Create the file
dex-config.yamlwith the following dex configuration:dex-config.yamlingress:
enabled: true
hosts:
- host: dex.yourcompany.tld # Use $DEX_HOSTNAME
paths:
- path: /
config:
issuer: https://dex.yourcompany.tld # "https://" + $DEX_HOSTNAME
connectors:
- {YOUR_CONNECTOR_CONFIG} # SEE LINKS BELOW! (do not remove the '-' and indent correctly)
staticClients:
- name: Loft
id: loft # Define a $DEX_CLIENT_ID
secret: XXXXXXXXXXXXXX # Define a $DEX_CLIENT_SECRET (can be any secret key)
redirectURIs:
- 'https://vcluster-platform.mycompany.tld/auth/oidc/callback' # vCluster Platform URL + /auth/oidc/callback
oauth2:
skipApprovalScreen: true
web:
http: 0.0.0.0:5556
storage:
type: kubernetes
config:
inCluster: trueCheck the official artifacthub.io page for all available options.
To fill the
connectorssection shown above, go to the appropriate docs page for the auth provider you want to use in combination with dex:Deploy Dex via Helm
After creating the file
dex-config.yaml, you can now install dex via Helm:helm install dex dex --repo https://charts.dexidp.io \
--create-namespace --namespace dex \
-f dex-config.yaml \
--waitConfigure the platform to use dex for authentication
To tell the platform to use dex for SSO, navigate to
Admin > Configin the platform and adjust your config as shown below:Platform OIDC config for dexauth:
oidc:
issuerUrl: https://dex.mycompany.tld # Use $DEX_HOSTNAME (see above)
clientId: "" # Use $DEX_CLIENT_ID (see above)
clientSecret: "" # Use $DEX_CLIENT_SECRET (see above)
type: "github" # Optional: SSO Login Button Icon ("", github, gitlab, microsoft, google)
usernameClaim: "email" # Optional: Which part of the dex token to use as vCluster Platform username (default: email)
usernamePrefix: "" # Optional: Add prefix to usernameClaim for vCluster Platform username
groupsClaim: "groups" # Optional: Add Kubernetes groups for this user
groupsPrefix: "loft-" # Optional: Prefix for Kubernetes groups
caFile: "" # Optional: Path to a CA cert of dex within the vCluster Platform container (default: '')Authenticate via dex + $OTHER_PROVIDER
After saving the new platform configuration, platform is going to restart itself and you should be able to log in via $OTHER_PROVIDER and dex.
Disable Username + Password Authentication (optional)
To turn off password-based authentication, navigate to
Admin > Configadd these two lines to your config:Disable password-based authenticationauth:
oidc: ... # This is your SSO configuration (make sure this is working!)
password:
disabled: true # Disable password-based authentication
Multiple SSO providers
In the Platform, you can also configure multiple SSO providers together. This can be a very handy feature if you have multiple groups using different authentication providers based on team or geographical region. Configuration of multiple SSO providers of the same type is also possible. The latter is configured by using the "connectors" option. Below is an example platform config "auth" section that contains three SSO providers (one OIDC, and two GitHub providers). Users logging into the platform with such a configuration present see three options for authentication as well as the default username/password box (which you can turn off if desired).
Add the following YAML configuration to your platform config (the config section of the values.yaml) or through vCluster Platform UI Admin > Config:
auth:
github:
clientId: test123
clientSecret: test123
redirectURI: https://my-vcluster-platform-url/auth/github/callback
oidc:
clientId: test
clientSecret: test
issuerUrl: https://example-issuer.com
redirectURI: https://my-vcluster-platform-url/auth/oidc/callback
# If you want to use multiple SSO configs of the same type you can use the connectors option
connectors:
# the id of the connector that will show up in the vcluster-platform callback url
- id: test
# name to show in the UI
displayName: Test GitHub
# any regular sso config
github:
clientId: test
clientSecret: test
# Make sure to exchange test here with the connector id if you change that
redirectURI: https://my-vcluster-platform-url/auth/test/callback
SSO group sync
The platform can be configured to allow user authentication via Single-Sign-On (SSO). SSO is an authentication method that enables users to access multiple applications with a single set of login credentials. This feature allows users with a valid account on another service (e.g., GitHub) to authenticate and log into the platform using that service. While this approach simplifies user management for administrators, a mechanism is still needed to ensure appropriate permissions are applied to these users. SSO groups address this need.
Most SSO providers allow administrators to configure data shared with
authenticating platforms. Among this shared data, the list of groups to which
the authenticating user belongs is particularly important. Upon SSO
authentication in the platform, this group data is inspected. The user is
automatically joined to any Teams that include any of the provided group names
in the SSO Groups as Members field. Any SSO group names not set in any Team's
SSO Groups as Members field is going to be dynamically created as a new Team, with the group name automatically set in the SSO Groups as Members field.
This group behavior allows administrators to create Teams in the platform that correspond to teams (groups) in the SSO identity provider, set the appropriate policy for those Teams, and enable users to be automatically assigned to the appropriate team, and thus privileges, upon logging in via SSO.
If a user belongs to multiple SSO groups that correspond to different Teams in the platform, they are going to be added to all matching Teams.
Create a team with SSO group membership
Select the Users field on the left menu bar.
Click the Teams button on the User Management screen.
Click the button.
In the drawer that appears from the right, give your new team a name by replacing the 'my-team' placeholder name, or by updating the manifest YAML 'metadata.name' field.
In the Team Members tab enter any desired groups into the SSO Groups as Members field. You can add as many groups as you would like here. These group names must exactly match the group name that the SSO provider shares with the platform during SSO authentication.
- Make any additional desired modifications to your new Team.
Click on the button.