Externally deployed virtual cluster
Virtual clusters can be classified into two main types based on their deployment method and management: platform deployed and externally deployed. Understanding the differences between these types is crucial for effective virtual cluster management and utilization of platform capabilities.
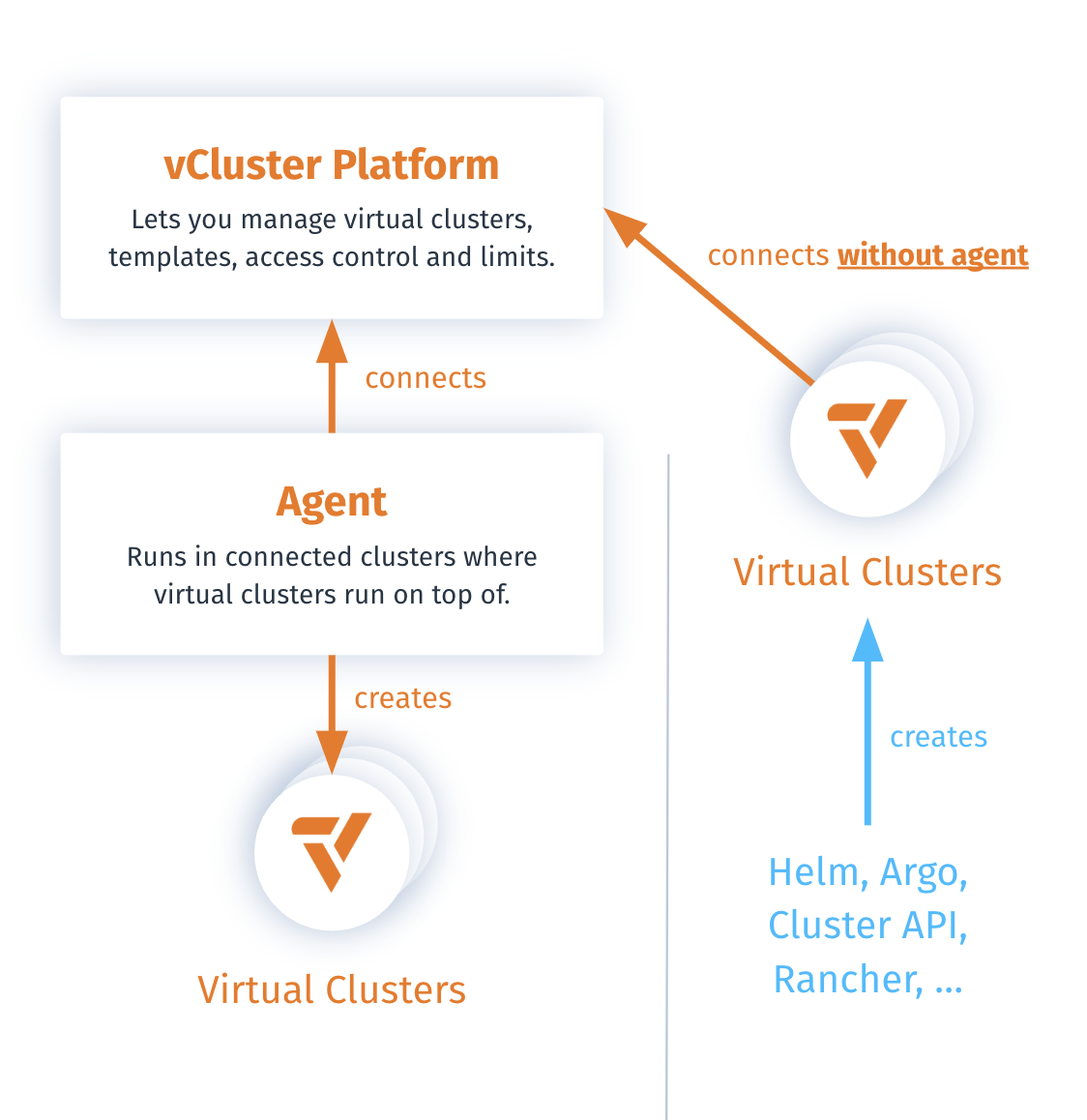
Platform deployed virtual clusters
Platform deployed virtual clusters are deployed and fully managed through the platform. They benefit from the platform's complete set of features and automated lifecycle management.
- Deployment methods:
- Platform UI
vCluster platform create vCluster <name>command
- Full platform lifecycle management and reconciliation
- Complete access to platform-specific features
Platform deployed clusters provide an integrated experience with centralized management and full platform feature utilization.
Externally deployed virtual clusters
Externally deployed virtual clusters are initially deployed outside of the platform, using tools like Helm, Argo, Terraform, or custom scripts. They can be added to the platform for enhanced management and feature access without changing their original deployment method.
- Deployed using external tools (e.g., Helm, Argo CD, ClusterAPI, Terraform)
- Added to the platform using
vCluster platform add vCluster [name]command - Platform does not manage lifecycle (no reconciliation)
- Allows use of certain platform features when connected with an agent
For externally deployed virtual clusters, lifecycle changes should be performed using the original deployment tool (e.g., Argo CD, ClusterAPI) rather than the platform UI.
Platform features for externally deployed virtual clusters
When an externally deployed virtual cluster is added to the platform and connected with an agent, certain platform features become available:
- Auto sleep (requires agent and vCluster.yaml configuration)
- Pro features of vCluster (license key distribution)
- Administrative overview of virtual cluster fleet
- UI-based inspection of cluster versions, enabled features, and resources
- Issue detection (e.g., vCluster errors, outdated Kubernetes versions)
- Enhanced debugging information and health status monitoring
- User access management through the platform (useful with SSO)
- Platform integrations (e.g., Argo CD, Vault secrets)
Features in the platform: section of the vcluster.yaml are only available if the agent is installed.
Understand the differences
Virtual clusters are classified based on two key factors:
- Creation method: Via the platform or external tools
- Management approach: Fully platform-managed or externally managed with optional platform features
- Lifecycle management: Platform-driven vs. externally controlled
- Feature availability: Full platform features vs. selective feature access (with agent)
Choose the deployment model
The choice between platform deployed and externally deployed virtual clusters can be made on a per-project or per-vCluster basis, allowing for a mix-and-match approach.
Consider the following factors:
- Existing Infrastructure: If you already use tools like Argo CD for virtual cluster management, you might prefer externally deployed clusters for those specific projects.
- Integration Needs: For projects requiring tight integration with all platform features, platform deployed clusters might be more suitable.
- Management Preferences: Some teams might prefer the centralized management of platform deployed clusters, while others might opt for the flexibility of externally deployed clusters with selective platform feature usage.
Remember, you can use both types within the same environment, choosing the most appropriate option for each virtual cluster based on its specific requirements and your team's preferences.
Add externally deployed clusters to the platform
To add an existing virtual cluster to the platform without changing its lifecycle management:
- Ensure the virtual cluster is running vCluster v0.20 or greater.
- Run the following command:
vcluster platform add vcluster [name]
This action is non-invasive and easily reversible, allowing you to benefit from platform features while maintaining your existing deployment workflows.
Next steps
- Create a virtual cluster in the platform.
- Add externally deployed virtual cluster virtual clusters to the platform.