What is vCluster?
| Enterprise | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Available in these plans | Free | Dev | Prod | Scale |
| Virtual Cluster Management | ||||
vCluster is an open source solution that enables teams to run virtual Kubernetes clusters inside existing infrastructure. It helps platform engineers create secure, isolated environments for development, testing, CI/CD, and even production workloads, without the cost or overhead of managing separate physical clusters.
vCluster supports a wide range of tenancy models, from lightweight namespace-based setups to more advanced configurations with private nodes, GPUs, and bare metal. Environments are defined declaratively, allowing teams to provision repeatable clusters that match their isolation and performance needs.
By consolidating workloads onto fewer host clusters, vCluster reduces infrastructure sprawl, lowers Kubernetes costs, and simplifies multi-tenant platform operations.
All vCluster features
vCluster provides a comprehensive set of features across multiple product tiers, from open source capabilities to enterprise-grade features. The table below shows all available features, their product tier availability (OSS, Free, Dev, Prod, Scale, Enterprise), and compatibility with different tenancy models (Shared Nodes, Private Nodes, Standalone).
What is a virtual cluster?
A virtual clusterVirtual ClusterA certified Kubernetes distribution that runs as an isolated, virtual environment nested inside a physical host cluster. Virtual clusters run inside host cluster namespaces but operate as independent Kubernetes environments, each with its own API server, control plane, syncer, and set of resources. is a fully functional Kubernetes cluster that runs on top of another Kubernetes cluster.
Typically, a virtual cluster runs inside a namespace of a host clusterHost ClusterThe physical Kubernetes cluster where virtual clusters are deployed and run. The host cluster provides the infrastructure resources (CPU, memory, storage, networking) that virtual clusters leverage, while maintaining isolation between different virtual environments., but it operates as an independent environment, with its own API server, control plane, and resource set.
Depending on the tenancy model, virtual clusters may share or isolate compute and networking resources. Regardless of the underlying setup, they remain abstracted from the host cluster’s global state, enabling strong workload separation and tenant autonomy.
vCluster extends this concept to support a full spectrum of tenancy models, from simple namespace syncing to advanced configurations using shared nodes, dedicated nodes, virtual nodes, private nodes or as a standalone Kubernetes cluster.
Virtual clusters are certified Kubernetes distributions, adhering to upstream Kubernetes standards while maintaining isolation from the host cluster.
This flexibility allows you to select the ideal tenancy model for your team’s security, cost, and performance requirements, while also benefiting from faster provisioning and centralized management.
Tenancy models overview
vCluster supports a range of tenancy models, allowing you to choose the right balance of isolation, cost-efficiency, and operational complexity for your platform. Each virtual cluster runs on top of a host Kubernetes cluster, but how it isolates workloads, consumes resources, and interacts with the underlying infrastructure depends on the tenancy model you select.
Below are the tenancy models supported by vCluster:
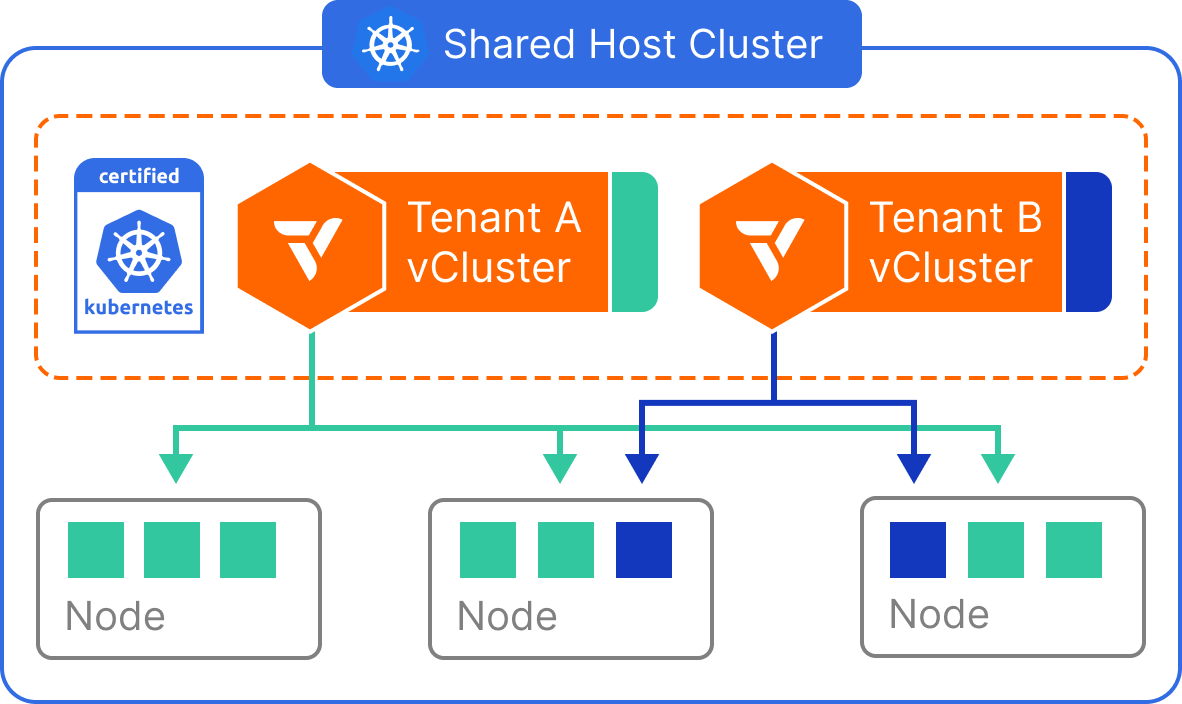
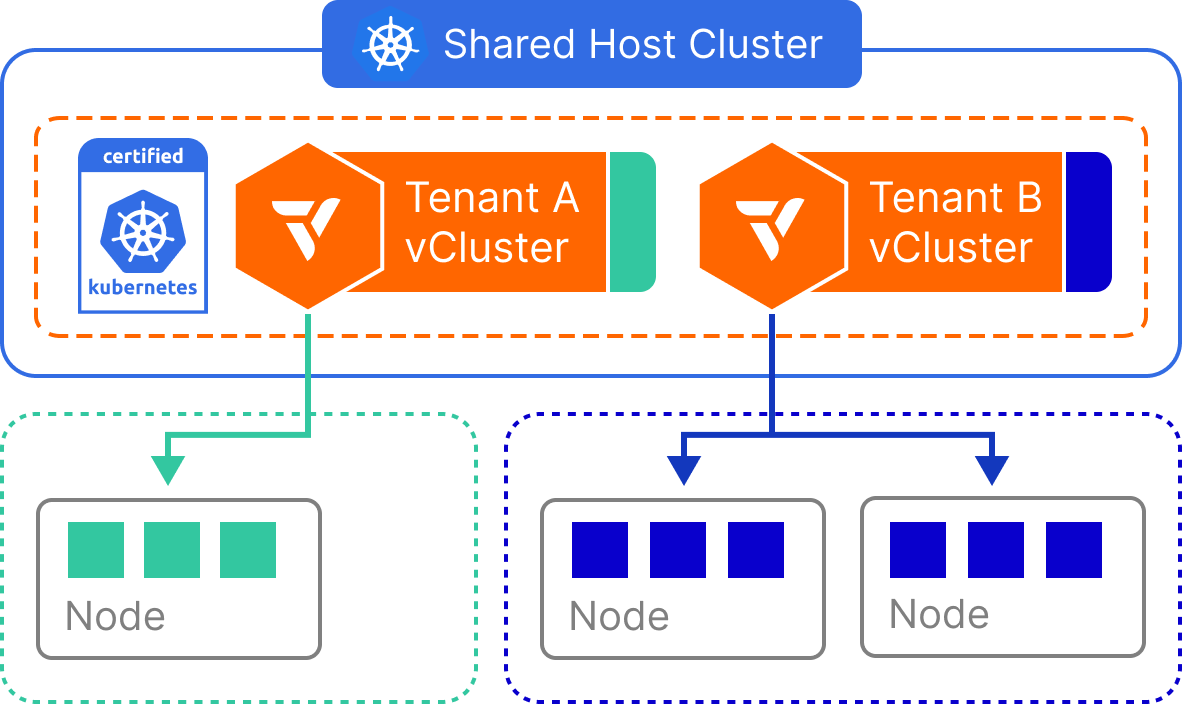
Shared Nodes
- The control plane of the vCluster is deployed as a container on a host cluster.
- Worker nodes of the vCluster are from the same host cluster.
How it works
All virtual clusters run in a single Kubernetes host cluster and schedule pods onto the same shared node pool. The vCluster control plane enforces separation at the API, RBAC, and CRD levels, but does not restrict pod scheduling unless additional mechanisms (e.g., taints, affinities) are applied. Tenants interact with their own virtual clusters as if they are separate environments, but their workloads run side-by-side with those from other virtual clusters at the node level. Shared infrastructure components like the container runtime, CNI, and CSI drivers are used across all tenants.
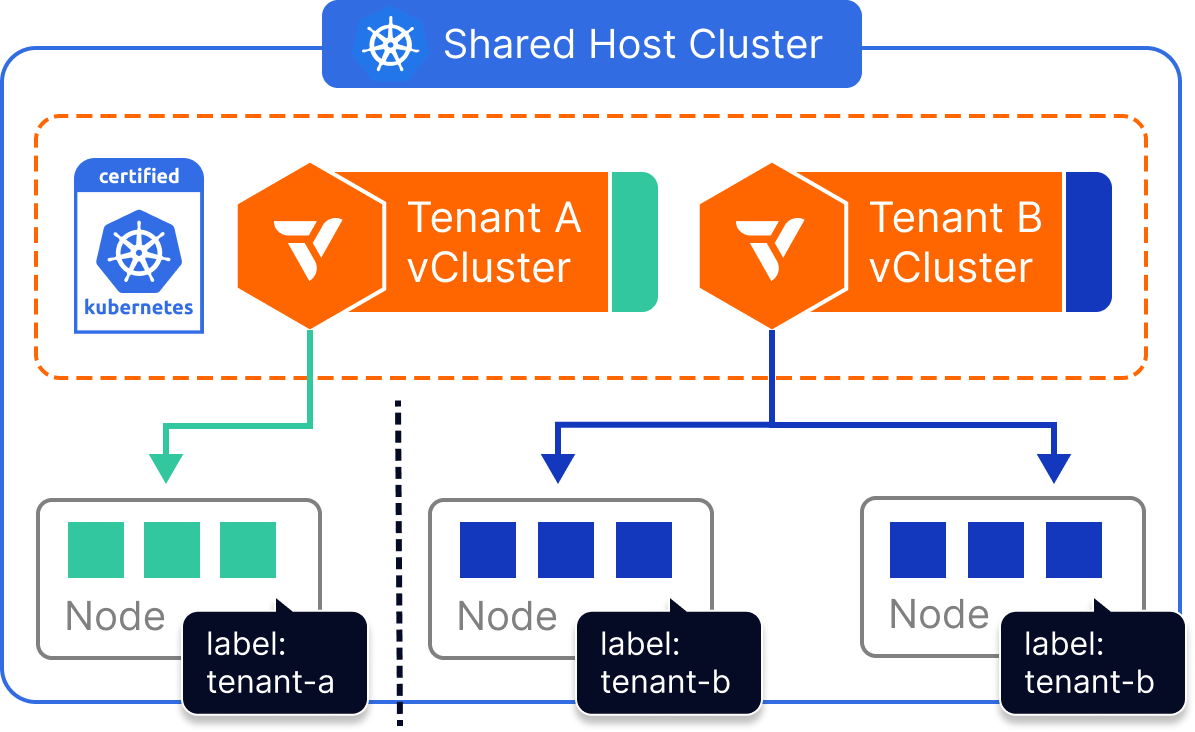
Dedicated Nodes
- The control plane of the vCluster is deployed as a container on a host cluster.
- Worker nodes of the vCluster are from a specific set of nodes of the same host cluster.
How it works
Each vCluster is configured with a Kubernetes nodeSelector (or affinity rules) that ensures all tenant workloads are scheduled only to nodes with specific labels. For example, a virtual cluster assigned to nodegroup=team-a will only run pods on nodes matching that label.
While compute is scoped to these dedicated nodes, all other components—like the CNI, CSI, and underlying Kubernetes host cluster—remain shared. The vCluster itself maintains full API isolation, separate CRDs, tenant-specific RBAC, and control plane security.
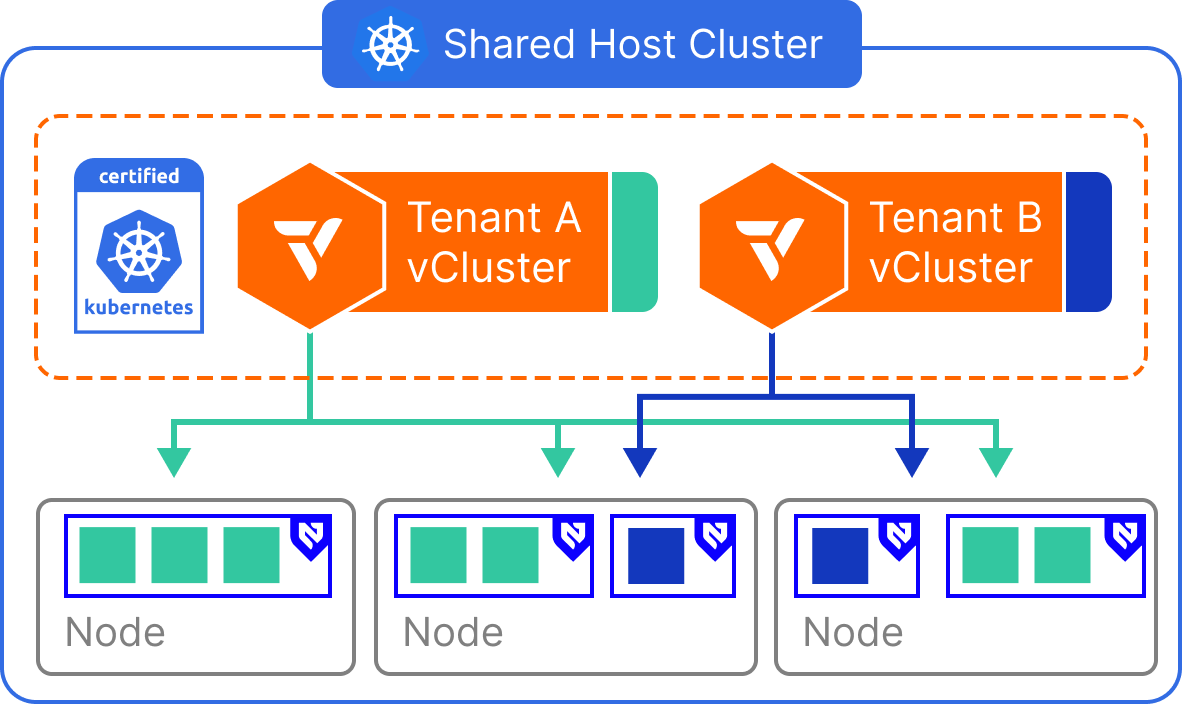
Virtual Nodes
- The control plane of the vCluster is deployed as a container on a host cluster.
- Worker nodes of the virtual cluster are running vNode on the set of nodes of the same host cluster.
How it works
Virtual Nodes are implemented within vCluster by inserting a translation layer between the virtual control plane and the physical cluster. From the perspective of a tenant, the vCluster presents one or more virtual nodes, each representing a safe, scoped execution environment.
Internally, workloads from these virtual nodes are scheduled as regular pods on shared physical nodes, but the tenant does not see or interact with the real underlying node environment. This abstraction enables stronger isolation, enforces placement boundaries, and prevents tenants from seeing or interacting with each other’s workloads—even though compute is technically shared.
Private Nodes
- The control plane of the vCluster is deployed as a container on a host cluster.
- Worker nodes of the vCluster are individual nodes that are not connected to any other Kubernetes cluster. You can either join manually provisioned nodes to a vCluster or can configure vCluster to automatically provision and join nodes based on resource requirements.
How it works
Each vCluster is deployed into its own Kubernetes host cluster, provisioned with a dedicated set of physical nodes. The CNI, CSI, kube-proxy, and all other Kubernetes components are fully isolated per tenant.
Because vCluster runs on top of this separate host cluster, it inherits the benefits of virtual cluster abstraction (faster startup, CRD freedom, sleep mode, etc.), but adds an additional hard isolation boundary beneath it. Tenants cannot interfere with one another’s environments at any layer—from API server to node kernel.
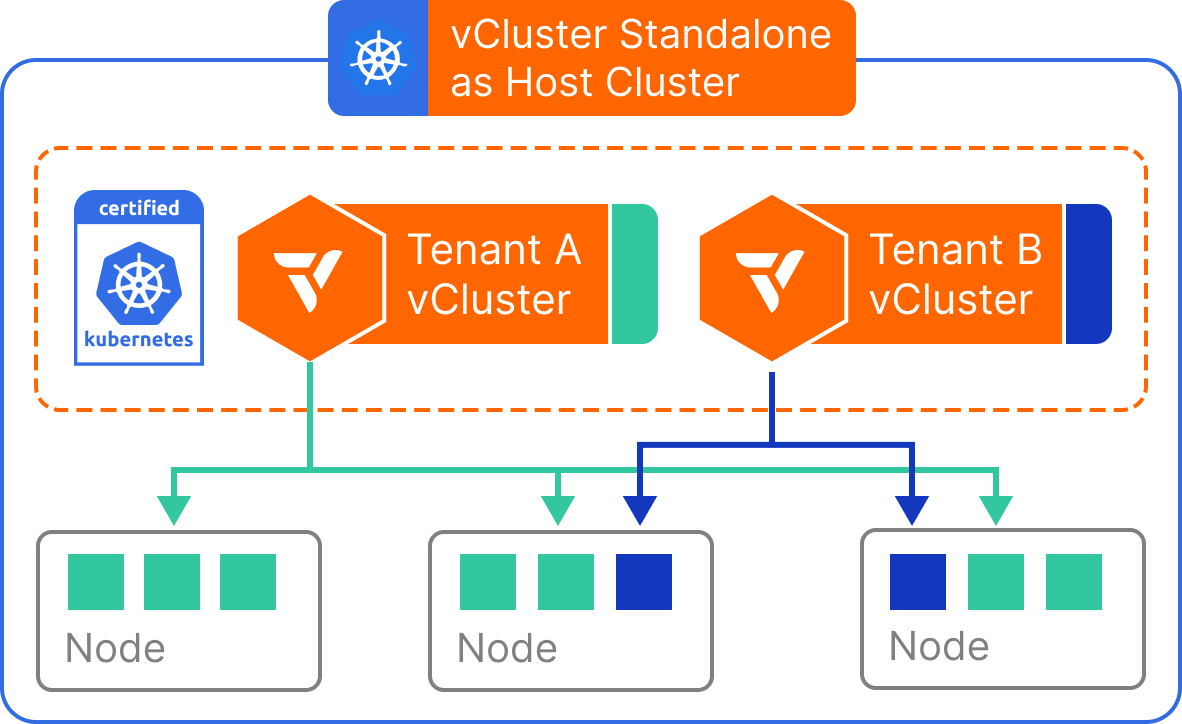
vCluster Standalone
- The control plane of the vCluster is deployed as a binary on individual nodes.
- Worker nodes of the vCluster are individual nodes that are not part of any other Kubernetes cluster.
How it works
vCluster Standalone launches its own lightweight control plane components (like an API server and scheduler) and backs workloads with a local Kubernetes-compatible runtime. Since no Kubernetes host cluster is required, virtual clusters can run independently in a container, virtual machine, or even on a developer laptop. Despite being self-contained, vCluster Standalone behaves just like a regular Kubernetes control plane: it supports custom resources, RBAC, workload scheduling, and even integrations with CI/CD tools. Workloads are managed entirely within the vCluster and does not require a host cluster to function.